World Diabetes Day: What Causes Diabetes, Types & More

Diabetes is often an unnoticed disease. Someone can be suffering from diabetes but have no evident symptoms. And often, by the time they’ve become aware of the disease, it has already advanced significantly.
But why does this happen? Simple, not everyone is familiar with what diabetes entails. Hence, early symptoms can be difficult to detect.
World Diabetes Day is commemorated every year on December 14th. World Diabetes Day is an excellent occasion to spread awareness about the disease. And that’s exactly what we’ll do.
In today’s post, we’ll share:
- What diabetes is
- What causes diabetes
- Which types of diabetes there are
- When you should get tested
Ready? Let’s dive in.
What Is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic health condition. It can appear at any age, due to various factors. In a nutshell, diabetes affects how food is converted into energy in your body.
Basically, your body digests most foods by breaking them down into sugar (glucose) and releasing it into your bloodstream. That’s how you get energy.
When your blood sugar levels rise, the pancreas releases insulin to regulate it.
In the body, insulin is like a key that allows blood sugar to enter your cells so it can be used as energy. However, it’s important to regulate glucose levels, to keep your cells functioning properly.
Diabetes occurs when your body doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t use it effectively. Consequently, your blood sugar levels will be too high.
Over time, this can lead to serious health problems, including:
- Heart disease
- Vision loss
- Hearing loss
- Kidney disease
- Nerve damage
- Foot health problems
As of today, there’s no cure for diabetes. But there are multiple things that you can do to address it or even prevent it, including:
- Eating a balanced diet
- Exercising frequently
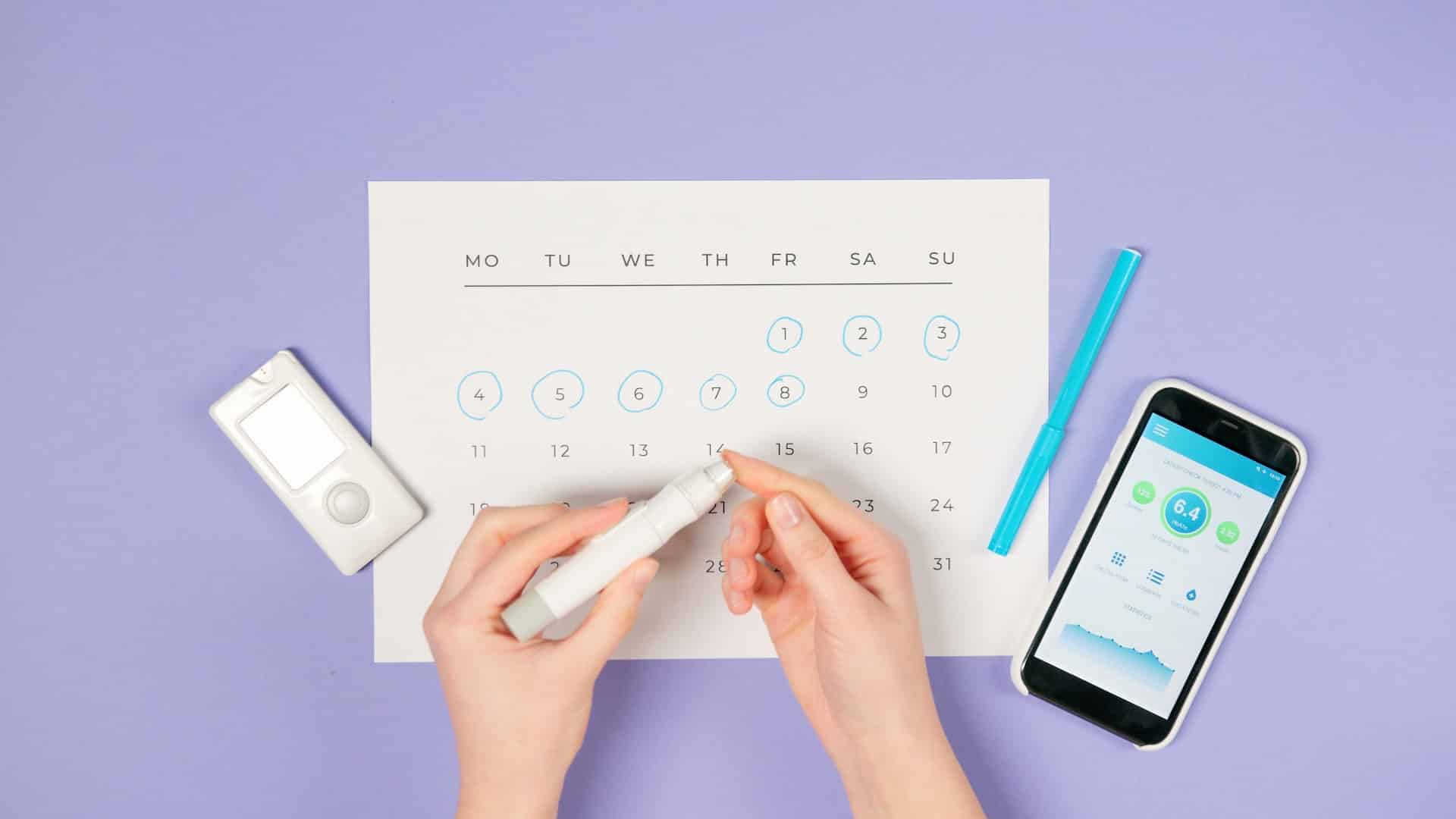
- Getting routine checkups regularly
What Causes Diabetes? [+ Diabetes Types]
There are 3 main types of diabetes:
- Type 1
- Type 2
- Gestational diabetes
Furthermore, there’s also a pre-stage of diabetes called prediabetes.
In this section, we’ll dive into each type of diabetes and explain its causes.
Prediabetes
Prediabetes is a stage previous to diabetes. Prediabetes is characterized by high blood sugar levels. But they’re not high enough to be diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Moreover, prediabetes increases your risk for:
- Type 2 diabetes
- Heart disease
- Stroke
In the USA, more than 1 in 3 people suffer prediabetes (96 million adults), and 8 in 10 aren’t aware of it. However, you can reverse prediabetes by following your doctor’s advice and making healthy lifestyle changes.
Type 1
Diabetes type 1 is believed to be caused by an autoimmune response. In other words, the body accidentally attacks itself and stops making insulin.
Type 1 diabetes affects about 5-10% of diabetics and there is often a rapid onset of symptoms. It’s usually diagnosed among children, teens, and young adults who have a family history of type 1 diabetes. Nevertheless, it’s worth mentioning that you can develop type 1 diabetes at any age.
People with type 1 diabetes need to take insulin every day. Moreover, there is no known way to prevent type 1 diabetes at the moment.
Type 2
When you have type 2 diabetes, your body doesn’t use insulin properly, and you can’t keep your blood sugar at a normal level.
Type 2 diabetes affects approximately 90-95% of diabetics. It usually develops over many years, in adults. But it’s been increasingly diagnosed in children, teens, and young adults as well. Type 2 diabetes symptoms may not be apparent.
Type 2 diabetes is more likely to develop if you:
- Have prediabetes
- Are overweight
- Are 45 years or older
- Aren’t physically active
- Ever had gestational diabetes, or given birth to a baby weighing more than 9 pounds
- Have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
If you’re at risk, you should get your blood sugar checked even if you don’t notice any symptoms.
It’s possible to prevent or delay type 2 diabetes by adopting a healthier lifestyle.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy. It develops in pregnant people who’ve never had diabetes. In most cases, it goes away after the baby is born. Nevertheless, it increases your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Additionally, your baby may face a higher risk of developing health problems later in life, including obesity and diabetes type 2.
You may develop gestational diabetes if:
- You are overweight
- You are over the age of 25
- You had gestational diabetes in the past
- You gave birth to a baby weighing more than 9 pounds
- You have a family history of type 2 diabetes
- You suffer from polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Preventing gestational diabetes may be possible by making lifestyle changes before you become pregnant. Getting regular physical activity, eating a healthy diet, and losing weight (if you’re overweight) can make a difference.
Diabetes Symptoms: When Should You Get Tested?
Diabetes symptoms vary across types. However, common symptoms include:
- Constant thirst
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Constant hunger
- Skin dryness
- Fatigue
- Losing weight without intending to
- Blurry vision
- Slow-healing sores
- A seemingly unjustified increase in infections
If you have any of these symptoms, you should consult your doctor to get your blood sugar tested. Moreover, every type of diabetes has unique symptoms. Let’s dive a little deeper.
Diabetes Type 1
Diabetes type 1 may also include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Stomach ache
Type 1 diabetes symptoms can develop within a few weeks or months and can be severe.
Diabetes Type 2
Type 2 diabetes symptoms often develop over several years. Some people don’t notice any symptoms at all. Generally, type 2 diabetes is diagnosed in adults.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes doesn’t usually show any symptoms. You should be tested for gestational diabetes by your doctor between weeks 24 and 28 of pregnancy.
Key Takeaways
Diabetes is a chronic disease that, if not properly treated, can lead to severe consequences. Hence, we highly recommend you get frequent doctor checkups and test your blood sugar levels.
Treatment will vary depending on your diagnosis. And contrary to what many may believe, diabetes doesn’t have to change your lifestyle drastically.
Want to get tested for COVID-19 before your next trip? Find COVID testing centers near you with our international directory.